In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, one of the most transformative innovations is personalized medicine—a model that shifts the “one-size-fits-all” approach to treatment towards care that’s uniquely tailored to each individual. At the core of this revolution lies genetics, the blueprint of our biological identity. By decoding this blueprint, researchers and clinicians are opening doors to more precise, effective, and safer treatments.
What Is Personalized Medicine?
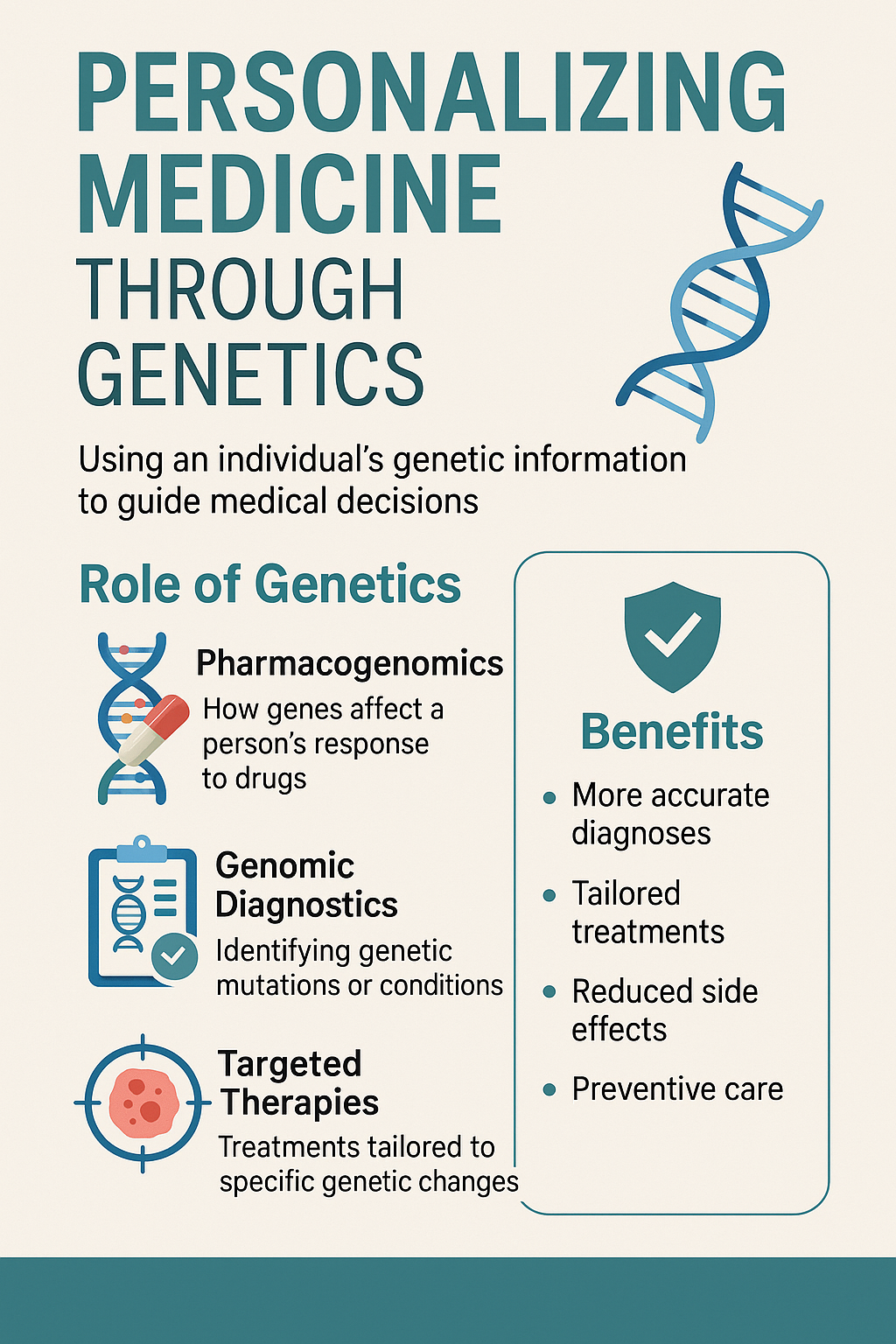
Personalized medicine—also referred to as precision medicine—is the practice of using an individual’s genetic information, along with other personal data, to guide decisions made in regard to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Instead of basing medical care solely on population averages, personalized medicine considers the unique genetic makeup of each patient.
The Role of Genetics in Personalized Medicine
Our genes influence how we respond to medications, our susceptibility to certain diseases, and even how diseases progress in our bodies. For example:
- Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs. This can help doctors prescribe the most effective medication with the least side effects.
- Genomic diagnostics can identify genetic mutations responsible for rare diseases or inherited conditions, leading to quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
- Targeted therapies in cancer treatment are a breakthrough application, where specific genetic mutations in a tumor are targeted with custom-designed drugs.
Real-World Applications
- Cancer Treatment: Modern oncology often uses genetic profiling of tumors to determine the best treatment plan. For instance, breast cancer patients with the HER2 gene mutation may benefit from targeted drugs like Herceptin.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Genetic testing can reveal inherited conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia, helping at-risk individuals begin early intervention.
- Mental Health: Genetic markers can help predict how patients might respond to psychiatric medications, enabling clinicians to avoid the painful trial-and-error process.
- Rare Diseases: Whole genome sequencing has led to diagnoses for patients who have spent years undiagnosed, sometimes leading to life-saving interventions.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- More accurate diagnosis
- Tailored and effective treatment plans
- Reduced risk of adverse drug reactions
- Enhanced preventive strategies
Challenges:
- Ethical concerns about genetic data privacy
- High cost of genetic testing and sequencing
- Need for healthcare providers trained in genomics
- Unequal access to personalized medicine technologies
The Future of Personalized Medicine
As genetic testing becomes more affordable and widespread, we can expect a future where every patient’s treatment is informed by their DNA. Artificial intelligence and big data are also playing a growing role, helping analyze complex genomic data to guide clinical decisions in real-time.
Initiatives like the All of Us Research Program in the U.S. and similar efforts worldwide are building vast genetic databases to fuel research and make personalized medicine more inclusive and impactful.
Conclusion
Personalized medicine, powered by genetics, represents not just a medical advancement but a paradigm shift in how we think about health. As we continue to unlock the secrets hidden in our genes, we edge closer to a world where treatment is not just reactive but predictive and preventive. In this era of genomic enlightenment, healthcare is becoming as unique as the individuals it serves.
Ms. Tejaswini Jagtap
Faculty Member at AISSMSCOP